Which of the following statements does not follow from the fact that the alkali metals have relatively weak metal–metal bonding? (a) The alkali metals are less dense than other metals. (b) The alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife. (c) The alkali metals are more reactive than other metals. (d) The alkali metals have higher melting points than other metals. (e) The alkali metals have low ionization energies.
The unit cell of a compound containing Co and O has a unit
cell shown below. The Co atoms are on the corners, and the O
atoms are completely within the unit cell. What is the empirical
formula of this compound? What is the oxidation state of
the metal?


Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Unit Cell Structure
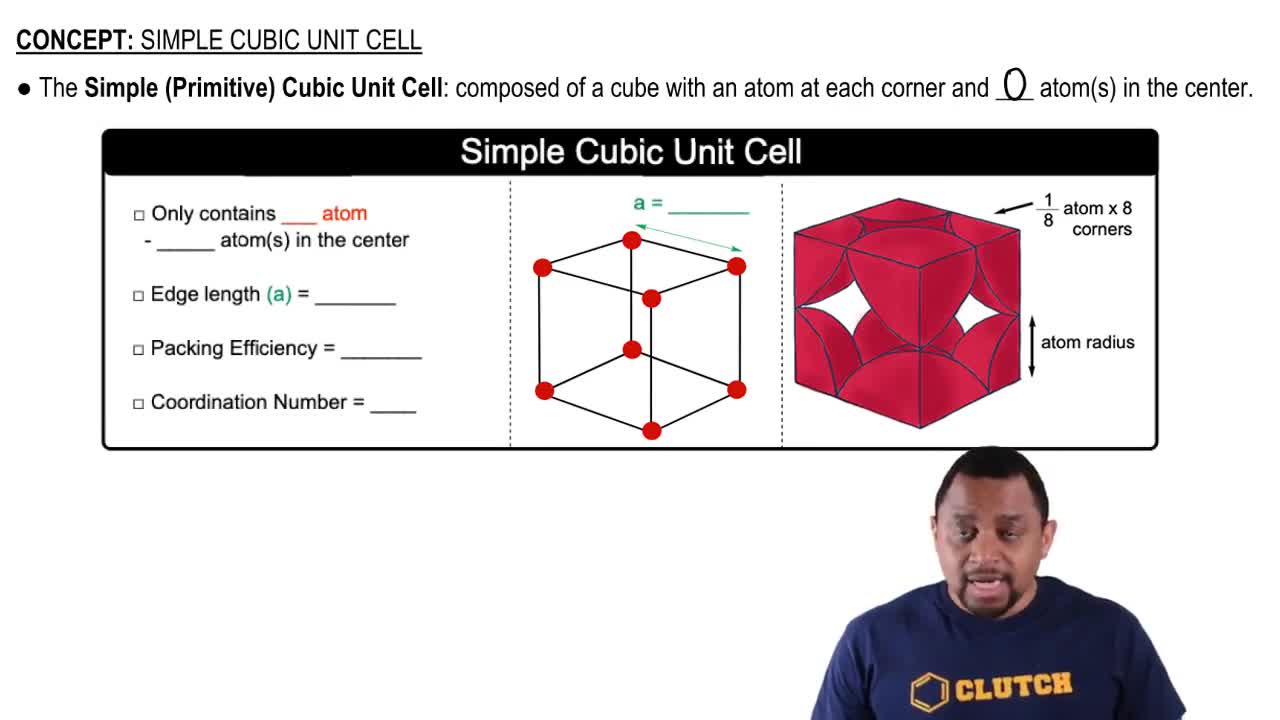
Empirical Formula

Oxidation State

Tausonite, a mineral composed of Sr, O, and Ti, has the cubic unit cell shown in the drawing. (a) What is the empirical formula of this mineral?
A particular form of cinnabar (HgS) adopts the zinc blende structure. The length of the unit cell edge is 5.852 Å. (b) The mineral tiemannite (HgSe) also forms a solid phase with the zinc blende structure. The length of the unit cell edge in this mineral is 6.085 Å. What accounts for the larger unit cell length in tiemmanite?
A particular form of cinnabar (HgS) adopts the zinc blende structure. The length of the unit cell edge is 5.852 Å. (c) Which of the two substances has the higher density? How do you account for the difference in densities?
CuI, CsI, and NaI each adopt a different type of structure. The three different structures are those shown in Figure 12.26. (a) Use ionic radii, Cs+ 1r = 1.81 A 2, Na+ 1r = 1.16 A 2, Cu+ 1r = 0.74 A 2, and, I- 1r = 2.06 A 2, to predict which compound will crystallize with which structure.
