Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
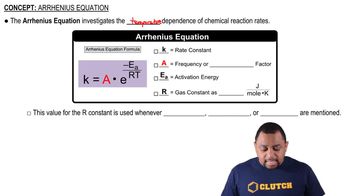
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation describes how the rate constant of a reaction depends on temperature. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This relationship indicates that as temperature increases, the rate constant typically increases due to higher molecular energy and more frequent effective collisions.
Recommended video:
Temperature Dependence of Rate Constants
Rate constants are temperature-dependent, meaning they change with variations in temperature. This dependence can be analyzed using the Arrhenius equation or by comparing rate constants at different temperatures. In this question, the rate constants at 400 K and 450 K are used to estimate the rate constant at an intermediate temperature of 425 K, highlighting the importance of understanding how temperature influences reaction kinetics.
Recommended video:
Kw Temperature Dependence
Linear Interpolation
Linear interpolation is a mathematical method used to estimate unknown values that fall within the range of known data points. In this context, it can be applied to find the rate constant at 425 K by using the known rate constants at 400 K and 450 K. This technique assumes a linear relationship between the two known points, allowing for a straightforward calculation of the desired value.
Recommended video:
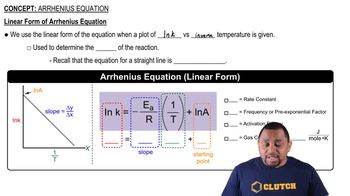
Linear Form of Arrhenius Equation