Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and pOH
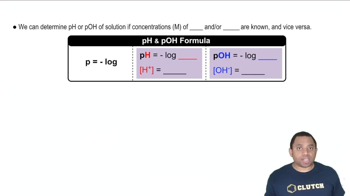
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. A pH of 7 is neutral, while values below 7 indicate acidity and above 7 indicate basicity. The relationship between pH and pOH is given by the equation pH + pOH = 14, allowing us to calculate pOH from pH and vice versa.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration
In basic solutions, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) can be derived from the pOH. The pOH is calculated as 14 - pH. Once the pOH is known, the hydroxide ion concentration can be found using the formula [OH-] = 10^(-pOH). This concentration is crucial for determining the concentration of the base in the solution.
Recommended video:
Hydroxide Ion Concentration Example
Stoichiometry of Calcium Hydroxide
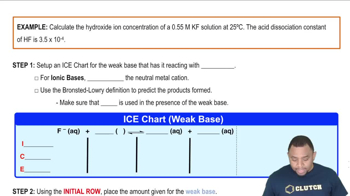
Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, dissociates in water to produce one calcium ion (Ca2+) and two hydroxide ions (OH-). The stoichiometry of this dissociation is important for calculating the concentration of the original compound based on the hydroxide ion concentration. If the concentration of OH- is known, the concentration of Ca(OH)2 can be determined by dividing the hydroxide concentration by 2.
Recommended video: