Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Addition Reactions
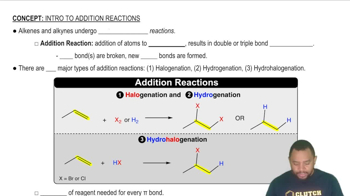
Addition reactions involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. In organic chemistry, these reactions often occur with unsaturated compounds, such as alkenes and alkynes, where π bonds are broken to allow new σ bonds to form. The reaction typically results in the saturation of the molecule, increasing the number of single bonds.
Recommended video:
Aldehydes and Their Reactivity
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain. They are highly reactive due to the electrophilic nature of the carbonyl carbon, making them susceptible to nucleophilic attack. In the presence of nucleophiles, such as HCN, aldehydes can undergo addition reactions to form new products, often resulting in the formation of cyanohydrins.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Aldehydes
Nucleophilic Addition
Nucleophilic addition is a fundamental reaction mechanism in organic chemistry where a nucleophile attacks an electrophilic center, typically a carbon atom in a carbonyl group. This process leads to the formation of a new bond and often results in the conversion of a carbonyl compound into an alcohol or other functional groups. In the case of the reaction with HCN, the cyanide ion acts as the nucleophile, adding to the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance