Textbook Question
What is the main global reservoir of nitrogen?
1011
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
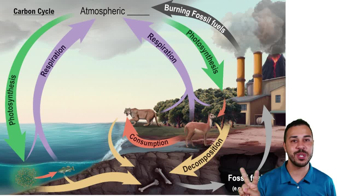


What is the main global reservoir of nitrogen?
True or False: Most of the net primary productivity that is consumed is used for growth by primary consumers. Explain.
In a model of the carbon cycle, how would you label an arrow from the atmosphere to plants?
a. cellular respiration
b. photosynthesis
c. decomposition
d. consumption
If the GPP of a grassland is 5000 kcal/m2/year and 55 percent is used up by cellular respiration, what is the NPP?
a. 2250 kcal/m2/year
b. 2750 kcal/m2/year
c. 5000 kcal/m2/year
d. Need more data
Explain why decomposition rates in a field in Nebraska would differ from the decomposition rates in a field in the Amazon. How do decomposers regulate nutrient availability in ecosystems?