Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
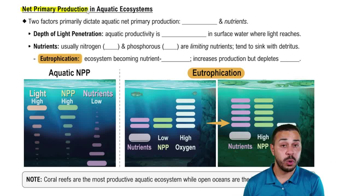
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) refers to the amount of organic matter or biomass produced by photosynthetic organisms, such as plants, after accounting for the energy used in respiration. It represents the energy available to support the next trophic levels in an ecosystem, including primary consumers. Understanding NPP is crucial for evaluating energy flow and ecosystem health.
Recommended video:
Primary Production in Aquatic Ecosystems
Primary Consumers
Primary consumers are organisms that feed directly on primary producers, typically herbivores that consume plants and algae. They play a vital role in the energy transfer within an ecosystem, as they convert the energy stored in plant biomass into forms that can be utilized by higher trophic levels. Their growth and reproduction depend on the availability of NPP.
Recommended video:
Primary Production in Aquatic Ecosystems
Trophic Levels
Trophic levels represent the hierarchical positions of organisms in a food chain, categorized by their feeding relationships. The first level consists of primary producers, followed by primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. Understanding trophic levels is essential for analyzing energy flow and the efficiency of energy transfer between different levels in an ecosystem.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance