During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? During athletic training, the oxygen–hemoglobin dissociation curve a. shifts to the right, unloading more oxygen to tissues. b. shifts to the right, unloading less oxygen to tissues. c. shifts to the left, unloading more oxygen to tissues. d. shifts to the left, unloading less oxygen to tissues.
During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? Explain the advantage of the observed difference between current athletes and non-athletes in the graph shown here.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Cardiovascular Adaptations to Exercise
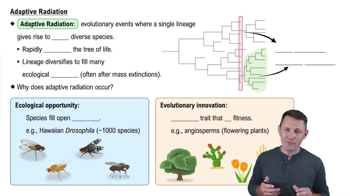
Oxygen Delivery and Utilization
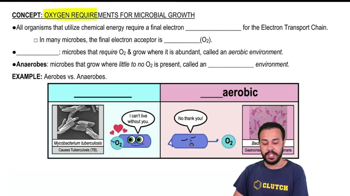
Physiological Differences Between Athletes and Non-Athletes

During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? When athletes exercise, what is the primary physiological variable responsible for their sustained increase in ventilation rate? a. decreased blood PO2 b. increased blood PCO2 c. increased blood pH d. increased body temperature
During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? Researchers used echocardiography, a sonogram of the heart, to estimate the mass of the left ventricle in current athletes, non-athletes, and ex-athletes. The data are graphed below (*** means P<0.001, and the P value comparing non-athletes and ex-athletes is >0.05). What conclusion can be drawn from the graph?
During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? Researchers have also observed that athletes and non-athletes have the same mean resting cardiac output, even though athletes have a far lower resting heart rate. How is this possible?
During exercise, the cardiovascular system must supply muscles with large amounts of oxygen and fuel and get rid of a lot of wastes. How do the cardiovascular systems of athletes respond to prolonged exercise? Athletes are not the only people with enlarged hearts. Many patients with cardiovascular disease also have enlarged hearts. Suggest a cause of this enlargement.
