What effect does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) have on the nephron? a. It increases water permeability of the descending limb of the loop of Henle. b. It decreases water permeability of the descending limb of the loop of Henle. c. It increases water permeability of the collecting duct. d. It decreases water permeability of the collecting duct.
The chloride cells of fish gills have a high density of mitochondria. How does this characteristic relate to the functional role of chloride cells? Would you expect other epithelial cells involved in ion transport to contain large numbers of mitochondria? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Chloride Cells
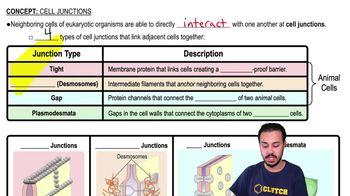
Mitochondria and Energy Production

Ion Transport in Epithelial Cells

Fill in the blank: In Gila monsters, the organ in which water from urine is reabsorbed into the bloodstream is the .
Compare and contrast the types of nitrogenous wastes excreted by animals. Identify which type can be excreted with the least water, which is most toxic, and which waste is excreted by bony fishes, by mammals, and by insects. Which type would you expect to be produced by embryos inside eggs laid on land?
Explain why mammals would not be able to produce concentrated urine if their nephrons lacked loops of Henle.
Scientists have noted that marine invertebrates tend to be osmoconformers, while freshwater invertebrates tend to be osmoregulators. Suggest an explanation for this phenomenon.
Biologists have been able to produce mice that lack functioning genes for aquaporins. How would the urine of these mice compare to that of mice with normal aquaporins? a. lower volume and lower osmolarity b. lower volume and higher osmolarity c. higher volume and lower osmolarity d. higher volume and higher osmolarity
