Scientists have noted that marine invertebrates tend to be osmoconformers, while freshwater invertebrates tend to be osmoregulators. Suggest an explanation for this phenomenon.
Fish and other aquatic organisms are exposed to many types of water pollutants, including metals such as aluminum. Although a low level of aluminum is found in unpolluted water, many lakes and streams have an increased level because of mining, sewage treatment, and accidental spills of toxic materials. Aluminum pollution can result in mass fish die-offs such as the one pictured here. How does this occur? Which of the following is an osmoregulatory challenge that freshwater fishes need to overcome? a. diffusion of sodium ions out of the body b. diffusion of water out of the body c. active transport of sodium ions out of the body d. active transport of water out of the body
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
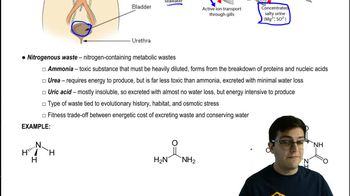
Osmoregulation
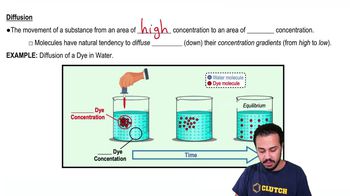
Diffusion
Active Transport

Biologists have been able to produce mice that lack functioning genes for aquaporins. How would the urine of these mice compare to that of mice with normal aquaporins? a. lower volume and lower osmolarity b. lower volume and higher osmolarity c. higher volume and lower osmolarity d. higher volume and higher osmolarity
To test the hypothesis that mussels are osmoconformers, researchers exposed mussels to water of varying osmolarities and then drew hemolymph samples from the mussels. Graph the data provided here. Put the independent variable on the x--axis and the dependent variable on the y-axis. Is the researchers' hypothesis supported by the data? Explain.
Fish and other aquatic organisms are exposed to many types of water pollutants, including metals such as aluminum. Although a low level of aluminum is found in unpolluted water, many lakes and streams have an increased level because of mining, sewage treatment, and accidental spills of toxic materials. Aluminum pollution can result in mass fish die-offs. In a laboratory, scientists exposed freshwater bony fish (Prochilodus lineatus) to water with a high level of aluminum and compared their blood osmolarity to that of fish exposed to water with a normal aluminum level (control). The results of the experiment are shown here (asterisks indicate P<0.05 between control and treated groups at a given time; BioSkills 3). Do the data support the hypothesis that aluminum interferes with osmoregulation in freshwater fishes? Explain.
Fish and other aquatic organisms are exposed to many types of water pollutants, including metals such as aluminum. Although a low level of aluminum is found in unpolluted water, many lakes and streams have an increased level because of mining, sewage treatment, and accidental spills of toxic materials. Aluminum pollution can result in mass fish die-offs. Why did the scientists do this experiment in a laboratory instead of simply collecting fish from a river with a high aluminum level and documenting their osmoregulatory ability?
Fish and other aquatic organisms are exposed to many types of water pollutants, including metals such as aluminum. Although a low level of aluminum is found in unpolluted water, many lakes and streams have an increased level because of mining, sewage treatment, and accidental spills of toxic materials. Aluminum pollution can result in mass fish die-offs. The scientists also measured the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase, in the gills of the fish exposed to aluminum and compared it to that of the control fish. What do you suppose were their results? Explain.
