Soils, water, and the atmosphere are major components of the abiotic (nonliving) environment. Describe how green plants affect the abiotic environment in ways that are advantageous to humans.
Angiosperms such as grasses, oaks, and maples are wind pollinated. The ancestors of these subgroups were probably pollinated by insects, however. As an adaptive advantage, why might a species 'revert' to wind pollination? (Hint: Think about the costs and benefits of being pollinated by insects versus wind.) Why is it logical to observe that wind-pollinated species usually grow in dense stands containing many individuals of the same species? Why is it logical to observe that in wind-pollinated deciduous trees, flowers form very early in spring—before leaves form?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Pollination Strategies

Cost-Benefit Analysis of Pollination

Flowering Phenology
The evolution of cuticle presented plants with a challenge that threatened their ability to live on land. Describe this challenge, and explain why stomata represent a solution. Compare and contrast stomata with the pores found in liverworts.
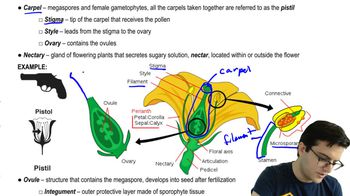
Explain the difference between homosporous and heterosporous plants. Where are the microsporangium and megasporangium found in a tulip? What happens to the spores that are produced by these structures?
You have been hired as a field assistant for a researcher interested in the evolution of flower characteristics in orchids. Design an experiment to determine whether color, size, shape, scent, or amount of nectar is the most important factor in attracting pollinators to a particular species. Assume that you can change any flower's color with a dye and that you can remove petals or nectar stores, add particular scents, add nectar by injection, or switch parts among species by cutting and gluing.
Moss sperm are motile and capable of swimming short distances to fertilize an egg. However, it was unknown until recently how sperm make their way from male to female gametophytes that may be separated by a distance of several centimeters or more. Researchers hypothesized that small animals called springtails (a type of arthropod) facilitate sperm transfer in mosses. To test this hypothesis, the researchers grew patches of male and female mosses at varying distances from each other and in the presence or absence of springtails. They later checked to see how many sporophytes were found in each female patch (as an indicator that fertilization had occurred). Their results are shown in the graph here (** means P<0.01, * means P>0.05. What conclusions can be drawn about the role of the springtails during the reproductive cycle of the mosses?
Moss sperm are motile and capable of swimming short distances to fertilize an egg. However, it was unknown until recently how sperm make their way from male to female gametophytes that may be separated by a distance of several centimeters or more. What structure do moss sperm use for motility, and how does that reflect the evolution of land plants from green algae?
