The vast majority of animals that ever existed are now extinct, but Tereza Jezkova and John Wiens wondered which variables were most important in driving the diversification of species that exist today. Why are there so many species in some phyla, such as Cnidaria, but so few in others, such as Ctenophora? Based on your reading of this chapter, propose at least five traits that you think might have been most important in triggering diversification within phyla (examples: origin of hearing, origin of internal fertilization).

Which traits do not correlate strongly with diversification rate within phyla but are likely to have been important in the original diversification of animal phyla during the Cambrian? Select True or False for each trait.
T/F presence of a head
T/F mobile lifestyle
T/F terrestrial lifestyle
T/F bilateral symmetry
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
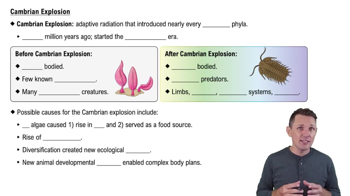
Cambrian Explosion
Diversification Rate

Bilateral Symmetry

The vast majority of animals that ever existed are now extinct, but Tereza Jezkova and John Wiens wondered which variables were most important in driving the diversification of species that exist today. Why are there so many species in some phyla, such as Cnidaria (see photo), but so few in others, such as Ctenophora? Jezkova and Wiens used a type of graph called a linear regression to find correlations between variables such as the proportion of species per phylum with legs (on the y-axis) and the diversification rate per phylum (on the x-axis). Sketch a graph to show what a strong positive correlation between these two variables would look like and what the absence of a correlation would look like.
The vast majority of animals that ever existed are now extinct, but Tereza Jezkova and John Wiens wondered which variables were most important in driving the diversification of species that exist today. Why are there so many species in some phyla, such as Cnidaria (see photo), but so few in others, such as Ctenophora? A sample of Jekova and Wiens' results is shown here. The R2 value represents the strength of the correlation (where 0.00 is lowest and 1.00 is highest). The P value represents the statistical significance. Which five traits look most important?
The vast majority of animals that ever existed are now extinct, but Tereza Jezkova and John Wiens wondered which variables were most important in driving the diversification of species that exist today. Why are there so many species in some phyla, such as Cnidaria (see photo), but so few in others, such as Ctenophora? The researchers know that correlation does not equal causation. However, can the absence of a correlation enable you to reject a hypothesis of causation? How would the R2 values be different in a scenario where a single trait was important to diversification in many phyla versus a scenario where different traits were important to diversification in different phyla?
