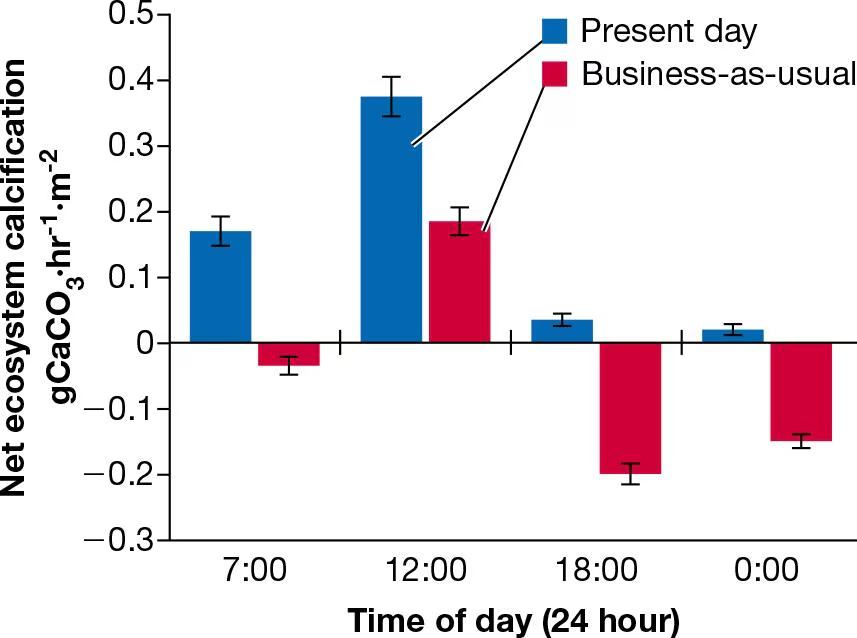
Consider the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid (CH2O3):
CO2(𝑔)+H2O(𝑙)⇌CH2O3(𝑎𝑞)
In the ocean, carbonic acid immediately dissociates to form a proton and bicarbonate ion, as follows:
CH2O3(𝑎𝑞)⇌CHO3−(𝑎𝑞)+H+(𝑎𝑞)
As atmospheric CO2 increases, the ocean absorbs more of the gas. Would this sequence of reactions be driven to the left or the right? How would this affect the pH of the ocean?