In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. List the genotype(s) of gametes produced by F1 individuals.

The smooth feathers on the back of the neck in pigeons can be reversed by a mutation to produce a 'crested' appearance in which feathers form a distinctive spike at the back of the head. A pigeon breeder examined offspring produced by a single pair of non-crested birds and recorded the following: 22 non-crested and 7 crested. She then made a series of crosses using offspring from the first cross. When she crossed two of the crested birds, all 20 of the offspring were crested. When she crossed a non-crested bird with a crested bird, 7 offspring were non-crested and 6 were crested. For these three crosses, provide genotypes for parents and offspring that are consistent with these results.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Genetics and Inheritance Patterns

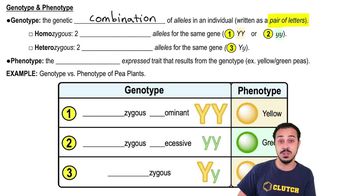
Phenotype and Genotype
Punnett Squares and Genetic Crosses

In garden peas, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y), and inflated pods (I) are dominant to constricted pods (i). Suppose you have crossed YYII parents with yyii parents. Draw the F2 Punnett square. Based on this Punnett square, predict the expected phenotype(s) in the F2 generation and the expected frequency of each phenotype.
In parakeets, two autosomal genes that are located on different chromosomes control the production of feather pigment. Gene B codes for an enzyme that is required for the synthesis of a blue pigment, and gene Y codes for an enzyme required for the synthesis of a yellow pigment. Green results from a mixture of yellow and blue pigments, and recessive mutations that prevent production of either pigment are known for both genes. Suppose that a breeder has two green parakeets and mates them. The offspring are green, blue, yellow, and albino (unpigmented).
Based on this observation, what are the genotypes of the green parents?
What genotypes produce each color in the offspring? What fraction of the progeny should exhibit each type of color?
The smooth feathers on the back of the neck in pigeons can be reversed by a mutation to produce a 'crested' appearance in which feathers form a distinctive spike at the back of the head. A pigeon breeder examined offspring produced by a single pair of non-crested birds and recorded the following: 22 non-crested and 7 crested. She then made a series of crosses using offspring from the first cross. When she crossed two of the crested birds, all 20 of the offspring were crested. When she crossed a non-crested bird with a crested bird, 7 offspring were non-crested and 6 were crested. Which allele is dominant?
Suppose you are heterozygous for two genes that are located on different chromosomes. You carry alleles A and a for one gene and alleles B and b for the other. Draw a diagram illustrating what happens to these genes and alleles when meiosis occurs in your reproductive tissues.
Suppose you are heterozygous for two genes that are located on different chromosomes. You carry alleles A and a for one gene and alleles B and b for the other. Label the stages of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, nonhomologous chromosomes, genes, and alleles.
