How is energy transferred among antenna pigment molecules? a. by heat b. by redox reactions c. by fluorescence d. by resonance
At what point in photosynthesis is the electromagnetic energy of light first converted into chemical energy?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
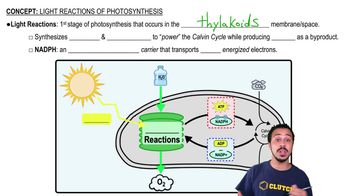
Key Concepts
Photosynthesis

Light-dependent Reactions
Chemical Energy

Why is chlorophyll green? a. It absorbs all wavelengths in the visible spectrum. b. It absorbs wavelengths only in the red portions of the spectrum (680–700 nm). c. It absorbs wavelengths only in the blue part of the visible spectrum (450–480 nm). d. It absorbs wavelengths in only the blue and red parts of the visible spectrum.
What is the role of PEP carboxylase in C4 and CAM plants? a. It fixes CO2 into an organic acid. b. It produces ATP for the Calvin cycle. c. It replaces rubicso in the Calvin cycle. d. It releases CO2 from organic acids.
Why is the chlorophyll in chloroplasts less likely to produce fluorescence compared to extracted chlorophyll molecules?
Describe the three phases of the Calvin cycle and how the products of the light-capturing reactions participate in this process.
Apply what you know of the relationship between the light-capturing reactions and the Calvin cycle to calculate the number of photons used to produce a new G3P and regenerate RuBP. (Assume 1 ATP is produced for each pair of electrons used to form NADPH.)
