Three of the following are evidence that charophytes are the closest algal relatives of plants. Select the exception. a. similar sperm structure b. the presence of chloroplasts c. similarities in cell wall formation during cell division d. genetic similarities in chloroplasts
Microphylls are found in which plant group? a. lycophytes b. liverworts c. ferns d. hornworts
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Microphylls
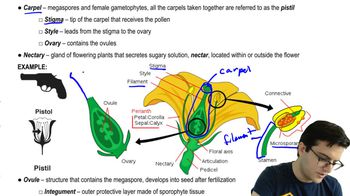
Lycophytes

Plant Classification

Which of the following characteristics of plants is absent in their closest relatives, the charophyte algae? a. chlorophyll b b. cellulose in cell walls c. sexual reproduction d. alternation of multicellular generations
In plants, which of the following are produced by meiosis? a. haploid gametes b. diploid gametes c. haploid spores d. diploid spores
Identify each of the following structures as haploid or diploid. a. sporophyte b. spore c. gametophyte d. zygote
EVOLUTION CONNECTION DRAW IT Draw a phylogenetic tree that represents our current understanding of evolutionary relationships between a moss, a gymnosperm, a lycophyte, and a fern. Use a charophyte alga as the outgroup. (See Figure 26.5 to review phylogenetic trees.) Label each branch point of the phylogeny with at least one derived character unique to the clade descended from the common ancestor represented by the branch point.
