Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Charophyte Algae
Charophyte algae are a group of green algae that are considered the closest relatives of land plants. They share several characteristics with plants, such as chlorophyll a and b, and cellulose in their cell walls. However, they lack certain complex features that define land plants, making them a crucial point of comparison in understanding plant evolution.
Recommended video:
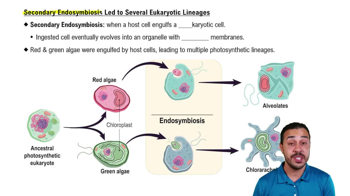
Secondary Endosymbiosis Led to Several Eukaryotic Lineages
Cellulose in Cell Walls
Cellulose is a polysaccharide that forms the primary structural component of plant cell walls. Both charophyte algae and land plants possess cellulose, which provides rigidity and support. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the structure of plant tissues, but it does not distinguish land plants from their algal relatives.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Bacterial Cell Walls
Alternation of Generations
Alternation of generations is a reproductive cycle in which a plant alternates between a haploid gametophyte stage and a diploid sporophyte stage. This complex life cycle is a defining feature of land plants, allowing for greater genetic diversity and adaptation. Charophyte algae typically do not exhibit this alternation, which highlights a significant evolutionary advancement in plants.
Recommended video:
Laminaria Life Cycle: Alternation of Generations