Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on their shared characteristics and genetic information. Each branch point, or node, indicates a common ancestor from which descendant species diverged. The tree helps visualize the evolutionary history and the relative timing of species' divergence.
Recommended video:
Building Phylogenetic Trees Example 2
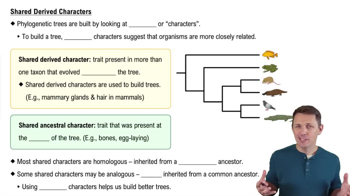
Derived Characters
Derived characters are traits that are present in a clade but absent in the last common ancestor of that clade. These traits are crucial for defining evolutionary relationships and are used to distinguish between different groups in a phylogenetic tree. Identifying derived characters helps clarify how species are related and the evolutionary adaptations that have occurred over time.
Recommended video:
Shared Derived Characters
Outgroup Comparison
An outgroup is a species or group of species that is closely related to the ingroup (the main group being studied) but not part of it. In phylogenetic analysis, outgroups are used to help determine the direction of evolutionary changes and to root the tree. By comparing the ingroup to the outgroup, researchers can identify which traits are ancestral and which are derived.
Recommended video:
Ingroups, Outgroups, & the Character Matrix

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance