Textbook Question
Which component is not directly involved in translation? a. GTP b. DNA c. tRNA d. ribosomes
1731
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
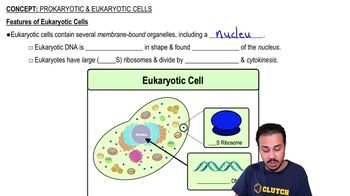


Which component is not directly involved in translation? a. GTP b. DNA c. tRNA d. ribosomes
Using Figure 17.6, identify a 5′→3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys. a. 5′-UUUCCCAAA-3′ b. 5′-GAACCCCTT-3′ c. 5′-CTTCGGGAA-3′ d. 5′-AAACCCUUU-3′
Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? a. a deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene b. a single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron c. a single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence d. a single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence
Complete the following table: