Which of the following areas of study focuses on the exchange of energy, organisms, and materials between ecosystems? a. organismal ecology b. landscape ecology c. ecosystem ecology d. community ecology
Which of the following is characteristic of most terrestrial biomes? a. a distribution predicted almost entirely by rock and soil patterns b. clear boundaries between adjacent biomes c. vegetation demonstrating vertical layering d. cold winter months
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
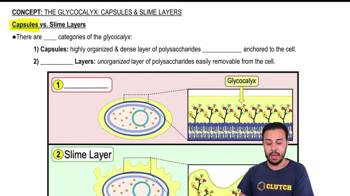
Key Concepts
Terrestrial Biomes

Vegetation Vertical Layering
Biome Boundaries

Which lake zone would be absent in a very shallow lake? a. benthic zone b. aphotic zone c. pelagic zone d. littoral zone
The oceans affect the biosphere by (A)absorbing a substantial amount of the biosphere's oxygen. (B)regulating the pH of freshwater biomes and terrestrial groundwater. (C)decreasing winter temperatures of coastal terrestrial biomes. (D)removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Which statement about dispersal is true? (A)Dispersal is not a component of the life cycles of most plants and animals. (B)Dispersal occurs only on an evolutionary time scale. (C)Colonization of devastated areas after floods or volcanic eruptions depends on dispersal. (D)The ability to disperse does not affect the geographic distribution of a species.
When climbing a mountain, we can observe transitions in biological communities that are analogous to the changes a. in biomes at different latitudes. b. in different depths in the ocean. c. in a community through different seasons. d. in an ecosystem as it evolves over time.
