Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
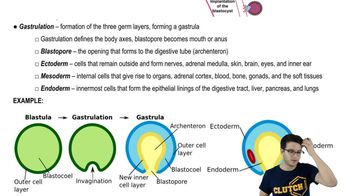
Gastrulation
Gastrulation is a crucial developmental process in embryology where the single-layered blastula reorganizes into a multi-layered structure called the gastrula. This process establishes the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which later differentiate into various tissues and organs. It is a defining characteristic of animal development, distinguishing animals from other life forms.
Recommended video:
Implantion and Gastrulation
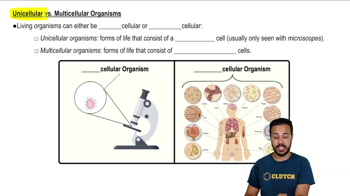
Multicellularity
Multicellularity refers to the condition of an organism being composed of multiple cells that work together to perform various functions. While many life forms, including plants and fungi, are multicellular, this characteristic is not unique to animals. However, the complexity of cellular organization and specialization in animals is a significant aspect of their biology.
Recommended video:
Unicellular vs. Multicellular
Flagellated Sperm
Flagellated sperm are a type of sperm cell characterized by the presence of a flagellum, which allows for motility. This feature is common in many animal species and is essential for sexual reproduction, as it enables sperm to swim towards the egg for fertilization. While flagellated sperm are prevalent in animals, they are also found in some protists and plants, making this characteristic not exclusive to animals.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance