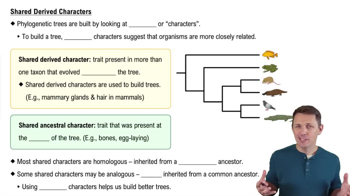
In a comparison of birds and mammals, the condition of having four limbs is a. a shared ancestral character. b. a shared derived character. c. a character useful for distinguishing birds from mammals. d. an example of analogy rather than homology.
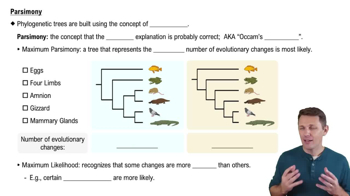
To apply parsimony to constructing a phylogenetic tree, a. choose the tree that assumes all evolutionary changes are equally probable. b. choose the tree in which the branch points are based on as many shared derived characters as possible. c. choose the tree that represents the fewest evolutionary changes, in either DNA sequences or morphology. d. choose the tree with the fewest branch points.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Parsimony in Phylogenetics
Shared Derived Characters
Phylogenetic Tree Construction

VISUAL SKILLS In Figure 26.4, which similarly inclusive taxon is represented as descending from the same common ancestor as Canidae? a. Felidae b. Mustelidae c. Carnivora d. Lutra
Three living species X, Y, and Z share a common ancestor T, as do extinct species U and V. A grouping that consists of species T, X, Y, and Z (but not U or V) makes up a. a monophyletic taxon. b. an ingroup, with species U as the outgroup. c. a paraphyletic group. d. a polyphyletic group.
.VISUAL SKILLS Based on the tree below, which statement is correct? (A)Lizards and goats form a sister group. (B)Salamanders are a sister group to the group containing liz-ards, goats, and humans. (C)Salamanders are more closely related to lizards than to humans. (D)Goats and humans are the only sister group shown in this tree.
