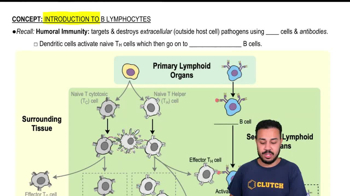
Humoral Immunity
Humoral immunity is a component of the adaptive immune system that involves the production of antibodies by plasma cells. These antibodies circulate in the bloodstream and bind to specific antigens, neutralizing pathogens or marking them for destruction by other immune cells. This type of immunity is crucial for defending against extracellular pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses.
Recommended video:
Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions, also known as allergic reactions, occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances, such as pollen or pet dander. In these reactions, antibodies, particularly IgE, bind to allergens and trigger the release of histamines and other chemicals from mast cells, leading to symptoms like itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Plasma cells play a role in producing these IgE antibodies.
Recommended video:
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders arise when the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the body's own tissues, perceiving them as foreign. This can lead to chronic inflammation and damage to various organs. Antibodies produced by plasma cells can contribute to these disorders by binding to self-antigens, which can disrupt normal physiological functions and lead to conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Problem 3
Problem 3 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance