Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Diffusion
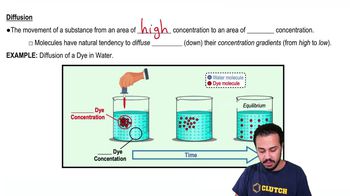
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In the context of nutrient and gas exchange, oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across capillary walls into and out of tissues, allowing for efficient transport of respiratory gases. This passive transport mechanism is crucial for maintaining cellular respiration and metabolic functions.
Recommended video:
Circulatory System
The circulatory system, comprising the heart, blood vessels, and blood, plays a vital role in transporting nutrients, wastes, and gases throughout the body. Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and returns carbon dioxide to be expelled. Additionally, it transports nutrients absorbed from the digestive system and removes metabolic wastes, ensuring homeostasis and proper organ function.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Organ Systems
Capillary Exchange
Capillary exchange refers to the process by which substances are transferred between blood and tissues through the thin walls of capillaries. This exchange occurs via mechanisms such as diffusion, filtration, and osmosis, allowing for the delivery of essential nutrients and the removal of waste products. The balance of hydrostatic and osmotic pressures in capillaries is critical for regulating fluid movement and maintaining tissue health.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Capillaries