Textbook Question
Describe the roles of each of the following components of the ECM:
d. Proteoglycans
291
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
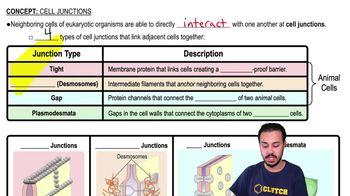


Describe the roles of each of the following components of the ECM:
d. Proteoglycans
Describe the roles of each of the following components of the ECM:
e. Glycoproteins (cell-adhesion molecules)
Describe the roles of each of the following components of the ECM:
f. Elastic fibers
Imagine that a disease turns the simple epithelia of the lungs, kidney tubules, and intestines into keratinized stratified squamous epithelia. What effect would this change in form have on the functions of these tissues?
Epithelial cells of the kidneys have pumps that drive the transcellular transport of sodium ions.
a. Is this epithelium likely to be simple or stratified? Why?