Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
d. Insulin secretion rises during feeding; growth hormone and glucagon are secreted during feeding if protein is present in the meal.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


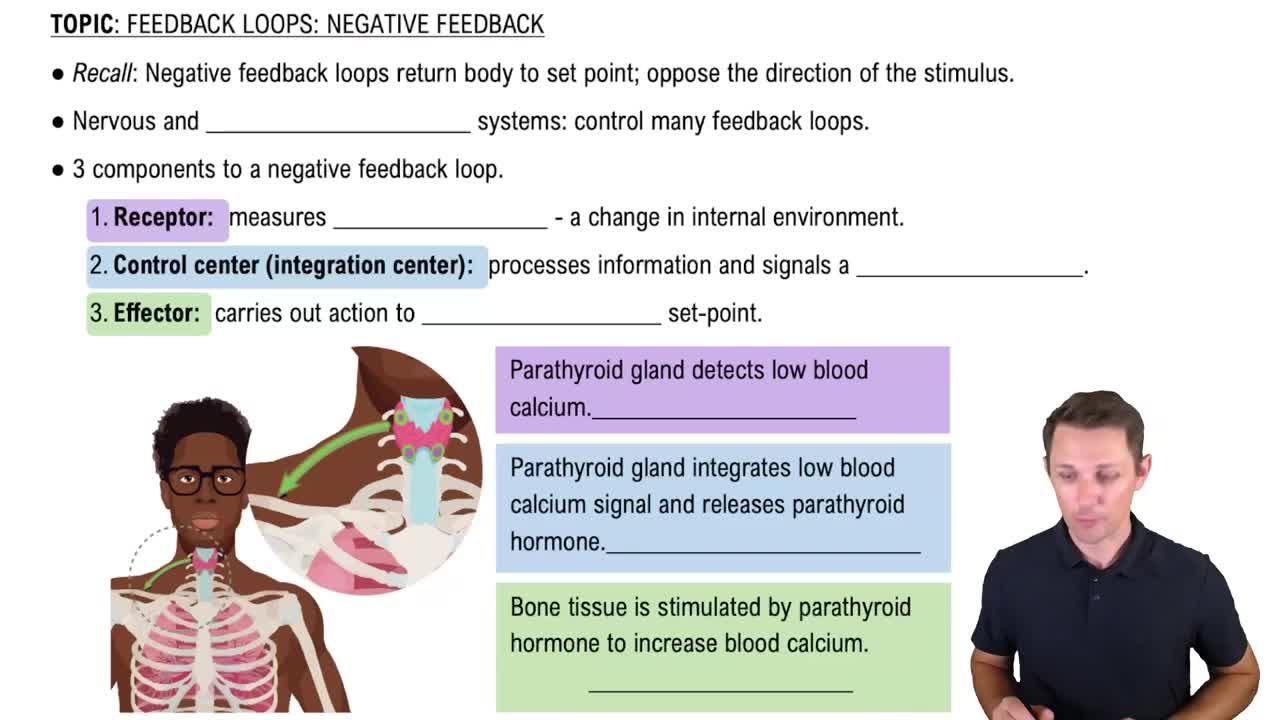
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
d. Insulin secretion rises during feeding; growth hormone and glucagon are secreted during feeding if protein is present in the meal.
Which of the following hormones is/are produced by the posterior pituitary?
a. Antidiuretic hormone
b. Oxytocin
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
A patient has a brain tumor that necessitates removal of his pituitary gland. Will its removal affect production of ADH and oxytocin? Explain.
How does ADH affect the amount of water in the body, and how does it accomplish this? How does this affect the osmolarity of the blood?
Mr. Montez is a patient with type I diabetes mellitus. He presents with dizziness, rapid breathing, confusion, and weakness. You find out that he forgot to inject his normal dose of insulin this morning. Will his blood glucose concentration be normal? Explain. Your colleague suggests that Mr. Montez needs to ingest some sugar. Is this going to help him? Why or why not?
Fill in the blanks: Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are released into the_____system and affect secretion from the_____gland.