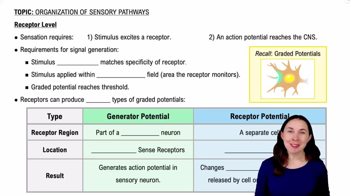
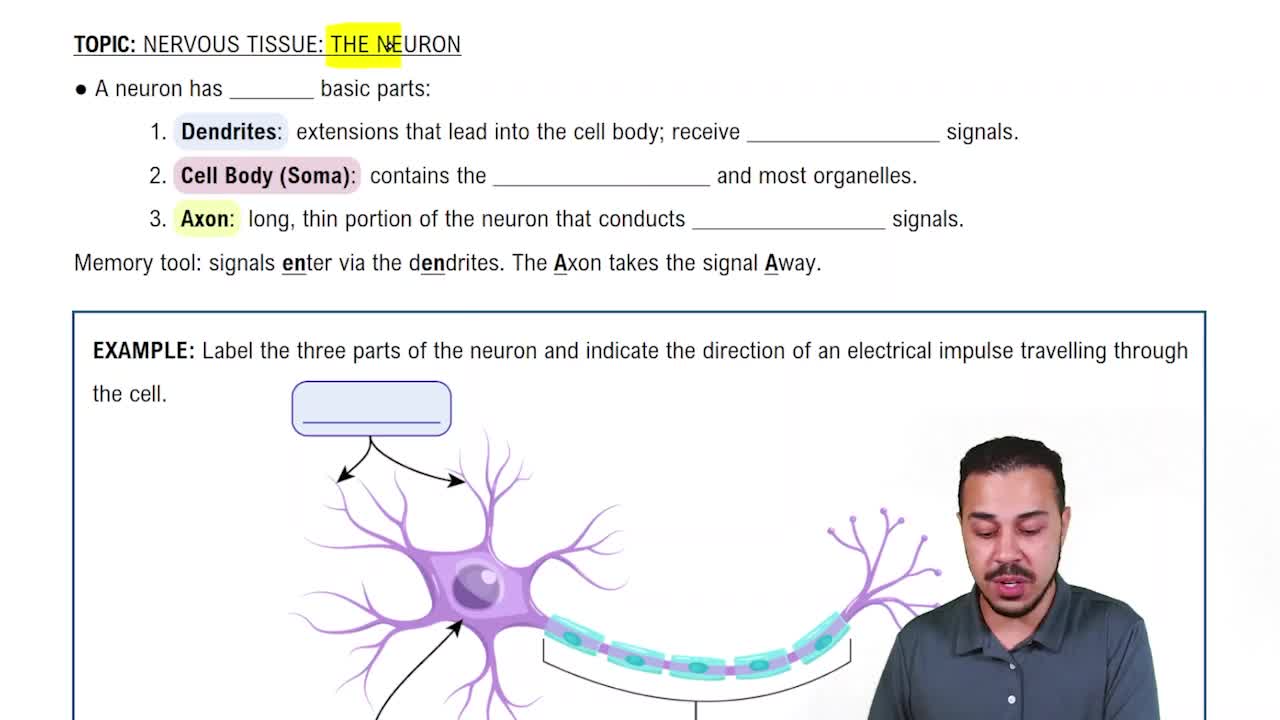
First, write the Roman numeral that corresponds to each named cranial nerve (after the abbreviation CN). Second, match the cranial nerve with its correct function from the column on the right.
CN____
______Vestibulocochlear nerve
CN____
______Trigeminal nerve
CN____
_______Hypoglossal nerve
CN____
_______Abducens nerve
CN____
_______Vagus nerve
CN____
_______Olfactory nerve
CN____
_______Accessory nerve
CN____
_______Oculomotor nerve
CN____
_______Facial nerve
CN____
_______Optic nerve
CN____
_______Glossopharyngeal nerve
CN____
_______Trochlear nerve
a. Motor to the lateral rectus muscle
b. Motor to the muscles of facial expression; lacrimation; salivation; taste to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue
c. Sense of smell
d. Motor to the muscles for swallowing; salivation; taste to the posterior one-third of the tongue; somatic sensation from the throat
e. Senses of hearing and equilibrium
f. Motor to the superior oblique muscle
g. Motor to the tongue
h. Motor to the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
i. Sense of vision
j. Motor to muscles of swallowing and speaking; parasympathetic innervation to thoracic and abdominal viscera; sense of taste from the throat
k. Sensory to the face; motor to the muscles of mastication
l. Motor to four of six extrinsic eye muscles; constricts the pupil; changes the shape of the lens; opens the eyelid