10. Parametric Equations
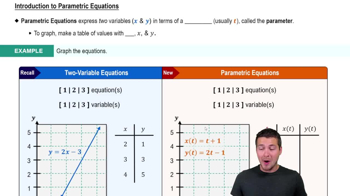
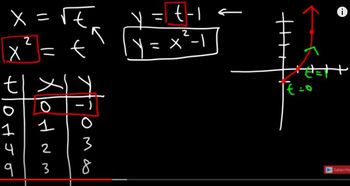
Graphing Parametric Equations
10. Parametric Equations
Graphing Parametric Equations
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Graph the plane curve formed by the parametric equations and indicate its orientation.
;
435views - Multiple Choice
Graph the plane curve formed by the parametric equations and indicate its orientation.
;
502views - Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, parametric equations and a value for the parameter t are given. Find the coordinates of the point on the plane curve described by the parametric equations corresponding to the given value of t.x = 3 − 5t, y = 4 + 2t; t = 1715views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, parametric equations and a value for the parameter t are given. Find the coordinates of the point on the plane curve described by the parametric equations corresponding to the given value of t.x = 7 − 4t, y = 5 + 6t; t = 1663views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, parametric equations and a value for the parameter t are given. Find the coordinates of the point on the plane curve described by the parametric equations corresponding to the given value of t.x = t² + 1, y = 5 − t³; t = 2769views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, parametric equations and a value for the parameter t are given. Find the coordinates of the point on the plane curve described by the parametric equations corresponding to the given value of t.x = t² + 3, y = 6 − t³; t = 2581views
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the graph of the parametric equations and as varies over all real numbers?
52views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the graph of the parametric equations and ?
57views