Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday's Law states that the electromotive force (emf) induced in a closed loop is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop. Mathematically, it is expressed as emf = -dΦ/dt, where Φ is the magnetic flux. This principle is fundamental in understanding how changing magnetic fields can generate electric currents.
Recommended video:
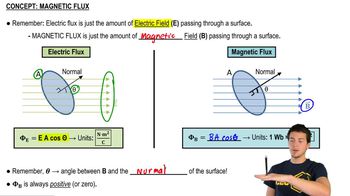
Magnetic Flux
Magnetic flux (Φ) is defined as the product of the magnetic field (B) and the area (A) through which the field lines pass, taking into account the angle (θ) between the field and the normal to the surface. It is given by the formula Φ = B * A * cos(θ). In this scenario, since the magnetic field is perpendicular to the loop, the angle is 0 degrees, simplifying the calculation.
Recommended video:
Lenz's Law
Lenz's Law states that the direction of the induced emf and the resulting current will be such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This law is a consequence of the conservation of energy and helps determine the polarity of the induced emf. In this case, as the magnetic field decreases, the induced current will flow in a direction that attempts to maintain the original magnetic field within the loop.
Recommended video: