Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. This relationship is expressed mathematically as V = I * R. Understanding this law is essential for calculating the current through each light bulb when connected in parallel.
Recommended video:
Resistors in Parallel
When resistors are connected in parallel, the total or equivalent resistance (R_eq) can be calculated using the formula 1/R_eq = 1/R1 + 1/R2. In this case, the voltage across each resistor remains the same, which is equal to the source voltage. This concept is crucial for determining how the current divides among the light bulbs based on their individual resistances.
Recommended video:
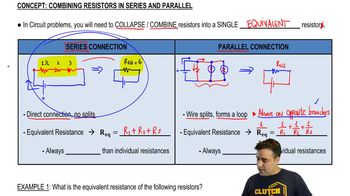
Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel
Current Division
Current division refers to the way current is distributed among parallel branches in a circuit. The current through each branch is inversely proportional to its resistance. For two resistors in parallel, the current through each can be calculated using the formula I_x = (V/R_x) for each resistor, where V is the voltage across the parallel combination. This principle is key to finding the current through each light bulb in the given problem.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance