Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Magnetic Field in a Solenoid
The magnetic field inside a long solenoid is given by the formula B = μ₀(nI), where B is the magnetic field strength, μ₀ is the permeability of free space, n is the number of turns per unit length, and I is the current. This relationship shows how the magnetic field strength is directly proportional to both the current flowing through the wire and the density of the turns.
Recommended video:
Magnetic Field Produced by Loops and Solenoids
Turns per Unit Length
Turns per unit length (n) refers to the number of loops of wire in a solenoid per unit of length. It is a crucial factor in determining the strength of the magnetic field produced by the solenoid. To find n, one can rearrange the magnetic field formula to n = B / (μ₀I), allowing for the calculation of the necessary turns to achieve a desired magnetic field.
Recommended video:
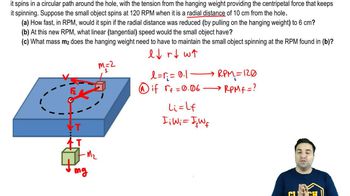
Spinning on a string of variable length
Permeability of Free Space
The permeability of free space (μ₀) is a physical constant that describes how a magnetic field interacts with a vacuum. Its value is approximately 4π × 10⁻⁷ T·m/A. This constant is essential in the calculation of magnetic fields in solenoids and other electromagnetic devices, as it influences the relationship between magnetic field strength, current, and turns per unit length.
Recommended video: