Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Kinetic Energy and Relativistic Effects
Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, calculated using the formula KE = (1/2)mv² for non-relativistic speeds. However, at high speeds, close to the speed of light, relativistic effects become significant, and the kinetic energy must be calculated using the relativistic formula KE = γmc² - mc², where γ (gamma) is the Lorentz factor. Understanding how to apply these concepts is crucial for determining the speed of the H- ion.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
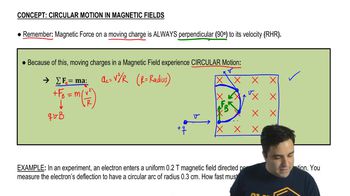
Magnetic Force and Circular Motion
When a charged particle moves in a magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force that acts perpendicular to its velocity, causing it to move in a circular path. The radius of this circular motion can be determined using the formula r = mv/(qB), where m is the mass, v is the velocity, q is the charge, and B is the magnetic field strength. This relationship is essential for calculating the radius of the H- ion's orbit in the cyclotron.
Recommended video:
Circular Motion of Charges in Magnetic Fields
Mass-Energy Equivalence
Mass-energy equivalence, expressed by Einstein's equation E=mc², indicates that mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. In the context of the H- ion, understanding how its mass relates to its energy is important, especially when considering the ion's kinetic energy at MeV levels. This concept helps in analyzing the behavior of particles in high-energy physics, such as those in cyclotrons.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy for Systems of Masses