Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity, is a measure of a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is defined as the ratio of the capacitance of a capacitor with the dielectric material to the capacitance of the same capacitor in a vacuum. A higher dielectric constant indicates a greater ability to store charge, which is crucial for understanding how materials affect the performance of capacitors.
Recommended video:
Energy Density in a Capacitor
Energy density in a capacitor refers to the amount of energy stored per unit volume of the dielectric material. It can be calculated using the formula U = 1/2 ε E², where U is the energy density, ε is the permittivity of the dielectric, and E is the electric field strength. This concept is essential for determining how much energy can be stored in a capacitor under specific electric field conditions.
Recommended video:
Energy Stored by Capacitor
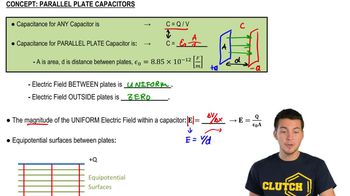
Capacitance and Plate Area
The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is directly related to the area of the plates and the distance between them, described by the formula C = ε(A/d), where C is capacitance, A is the area of the plates, d is the separation, and ε is the permittivity of the dielectric. Understanding this relationship is vital for calculating the required plate area when given energy storage and voltage conditions, as it allows for the design of capacitors to meet specific energy requirements.
Recommended video:
Parallel Plate Capacitors