Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carnot Cycle
The Carnot cycle is a theoretical thermodynamic cycle that provides the maximum possible efficiency for a heat engine or refrigerator operating between two temperature reservoirs. It consists of four reversible processes: two isothermal and two adiabatic. The efficiency of any real engine or refrigerator cannot exceed that of a Carnot cycle operating between the same temperatures.
Recommended video:
The Carnot Cycle and Maximum Theoretical Efficiency
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigerator or heat pump, defined as the ratio of the heat removed from the cold reservoir to the work input required to remove that heat. For a Carnot refrigerator, the COP can be calculated using the formula COP = T_c / (T_h - T_c), where T_c is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir and T_h is the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir.
Recommended video:
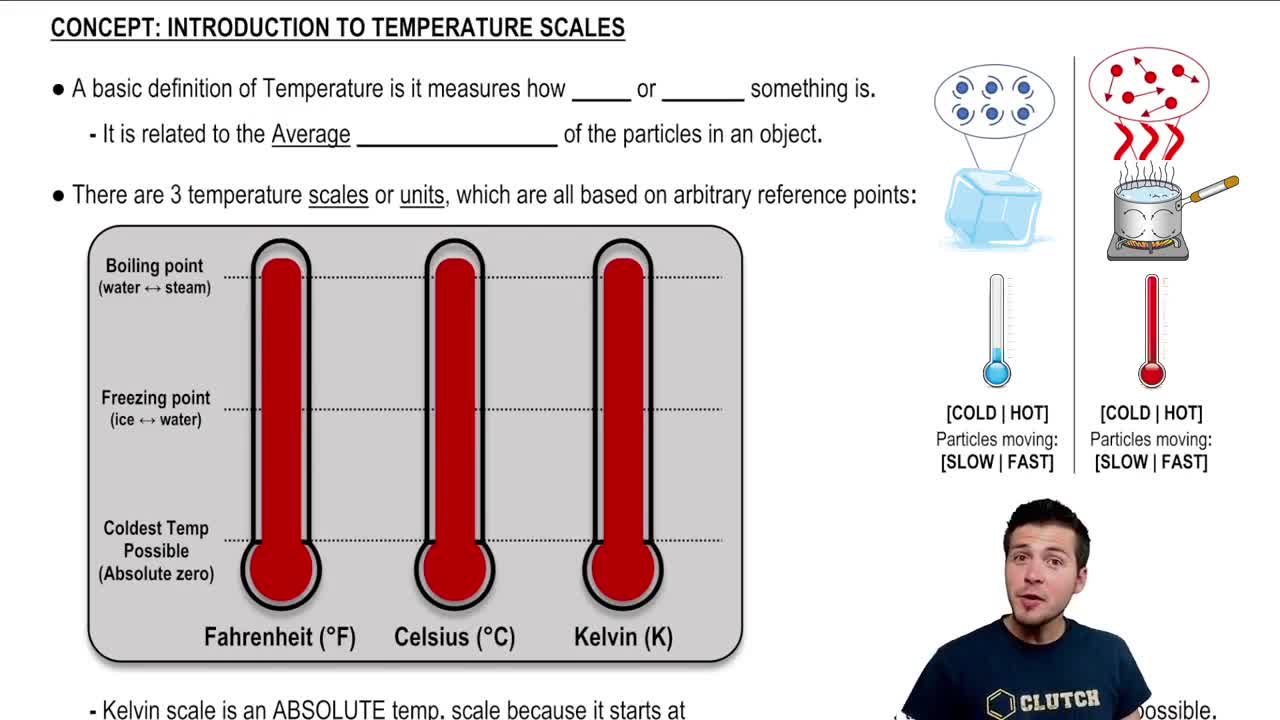
Thermodynamic Temperature Scale
The thermodynamic temperature scale is an absolute temperature scale based on the principles of thermodynamics, measured in Kelvin (K). It is crucial for calculations in thermodynamics because it avoids negative values and provides a direct relationship between temperature and energy. In the context of the Carnot refrigerator, temperatures of the heat reservoirs must be expressed in Kelvin to accurately determine the COP.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance