Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Carnot Engine
A Carnot engine is an idealized heat engine that operates on the reversible Carnot cycle. It is designed to achieve maximum efficiency by operating between two thermal reservoirs at different temperatures. The efficiency of a Carnot engine depends solely on the temperatures of the hot and cold reservoirs, making it a benchmark for real engines.
Recommended video:
Thermal Efficiency
Thermal efficiency is a measure of how well an engine converts heat energy from a fuel into work. It is defined as the ratio of the work output of the engine to the heat input from the hot reservoir. For a Carnot engine, the thermal efficiency can be calculated using the formula: η = 1 - (T_c / T_h), where T_c is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir and T_h is the absolute temperature of the hot reservoir.
Recommended video:
Thermal Efficiency & The Second Law of Thermodynamics
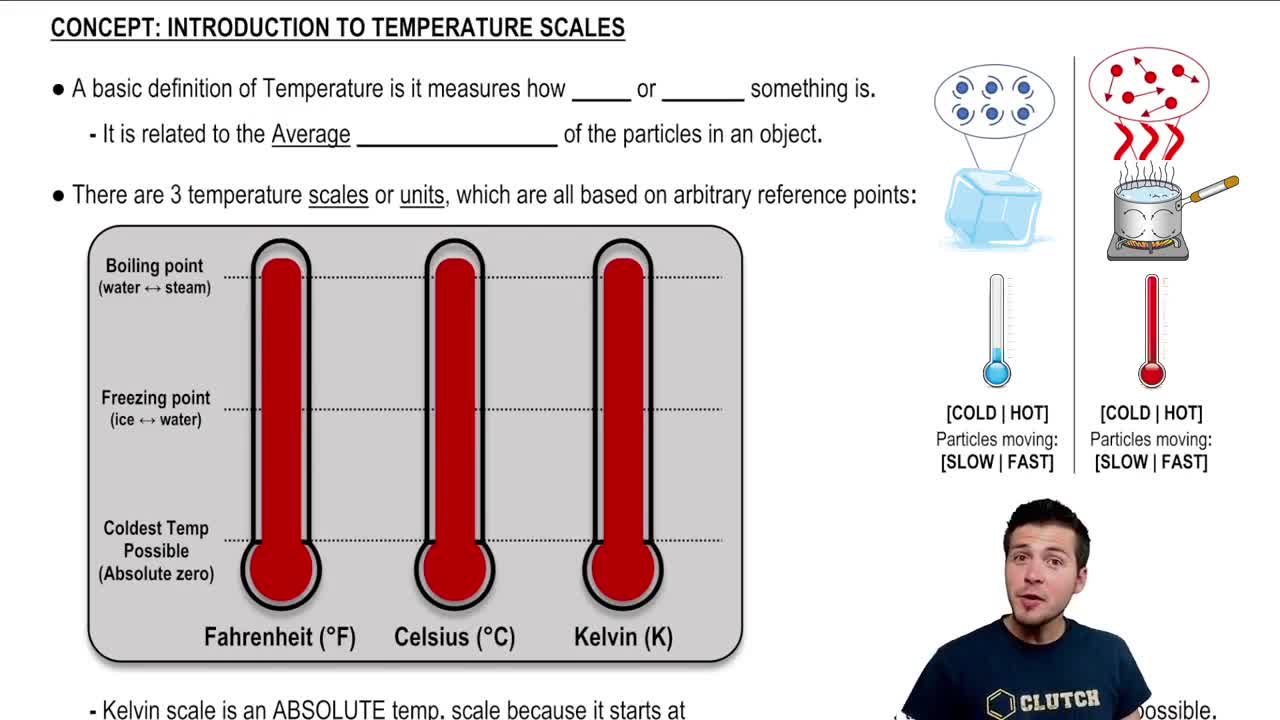
Absolute Temperature
Absolute temperature is a temperature measurement on the Kelvin scale, where 0 K represents absolute zero, the point at which molecular motion ceases. In thermodynamics, using absolute temperatures is crucial because it ensures that calculations involving thermal energy and efficiency are accurate. The Kelvin scale is used in the Carnot efficiency formula to maintain consistency in temperature measurements.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales