Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Temperature Scales
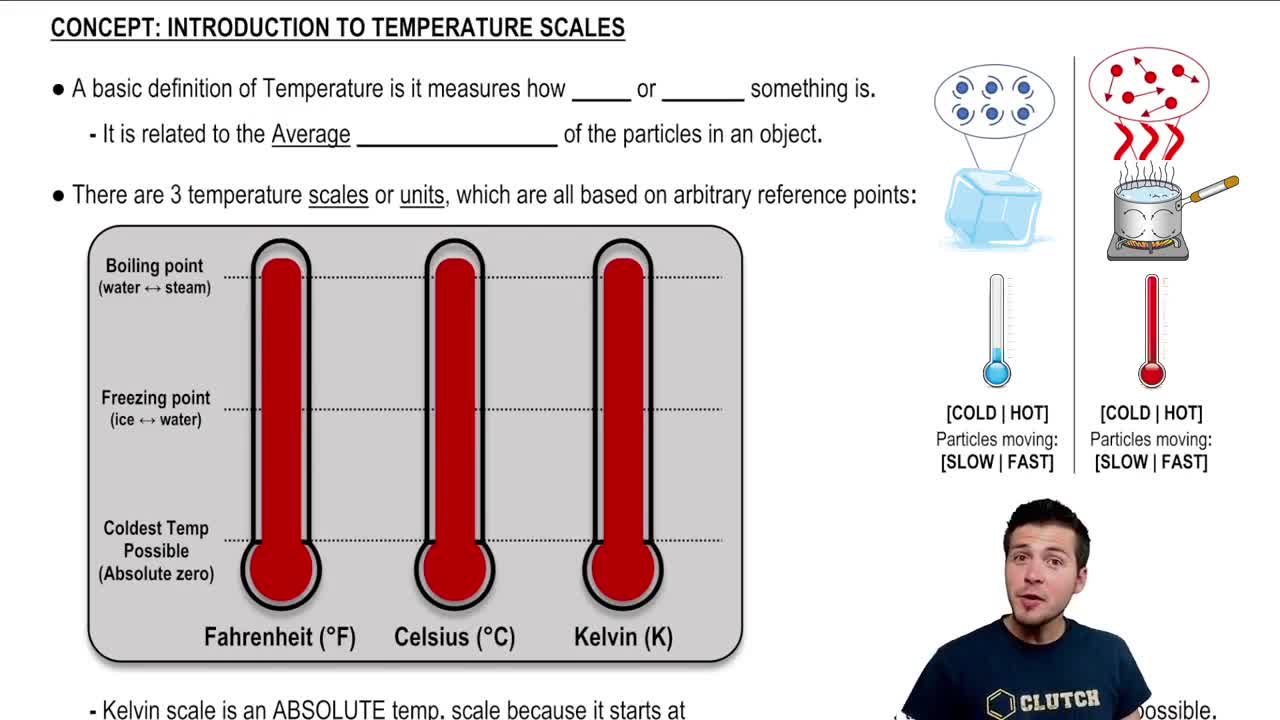
Fahrenheit and Celsius are two different temperature scales used to measure thermal energy. The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, set at 0°C and 100°C, respectively. The Fahrenheit scale, primarily used in the United States, sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F. Understanding the relationship between these scales is crucial for converting temperatures and finding points of agreement.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
Linear Equations
The relationship between the Celsius (C) and Fahrenheit (F) scales can be expressed as a linear equation: F = (9/5)C + 32. This equation allows for the conversion of temperatures from one scale to another. To find the temperature at which both scales agree, one must solve for the point where C equals F, leading to a single temperature value.
Recommended video:
Algebraic Manipulation
Algebraic manipulation involves rearranging and solving equations to isolate variables. In this context, to find the temperature where Celsius and Fahrenheit are equal, one must set the equations equal to each other and solve for the variable. This skill is essential for deriving the solution and understanding how different mathematical operations can be applied to real-world problems.
Recommended video:
Simplifying Algebraic Expression