Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
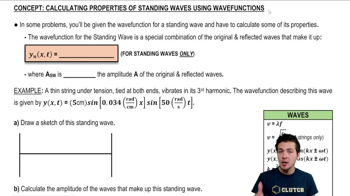
Wave Properties
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium without the permanent displacement of the medium itself. Key properties of waves include wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. The wavelength is the distance between successive crests or troughs, while frequency is the number of cycles that pass a point per unit time. Understanding these properties is essential for analyzing wave behavior.
Recommended video:
Properties of Standing Waves from Wave Functions
Relationship Between Wave Speed, Frequency, and Wavelength
The speed of a wave is related to its frequency and wavelength by the equation v = fλ, where v is the wave speed, f is the frequency, and λ is the wavelength. This relationship allows us to calculate one of these properties if the other two are known. For sound waves in air, the speed is approximately 343 m/s at room temperature, which can be used to find the wavelength when the frequency is given.
Recommended video:
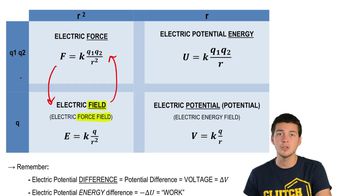
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Pressure Amplitude and Displacement Amplitude
In sound waves, the pressure amplitude is the maximum change in pressure from the ambient atmospheric pressure, while the displacement amplitude refers to the maximum displacement of particles in the medium from their equilibrium position. These amplitudes are related, as greater displacement leads to greater pressure variations. Understanding this relationship is crucial for analyzing how sound waves propagate through different media.
Recommended video:
Amplitude Decay in an LRC Circuit