A uniform bar has two small balls glued to its ends. The bar is 2.00 m long and has mass 4.00 kg, while the balls each have mass 0.300 kg and can be treated as point masses. Find the moment of inertia of this combination about an axis parallel to the bar and 0.500 m from it.

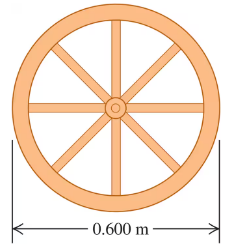
A wagon wheel is constructed as shown in Fig. E9.33. The radius of the wheel is 0.300 m, and the rim has mass 1.40 kg. Each of the eight spokes that lie along a diameter and are 0.300 m long has mass 0.280 kg. What is the moment of inertia of the wheel about an axis through its center and perpendicular to the plane of the wheel? (Use Table 9.2.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Moment of Inertia

Parallel Axis Theorem

Composite Bodies

You are a project manager for a manufacturing company. One of the machine parts on the assembly line is a thin, uniform rod that is 60.0 cm long and has mass 0.400 kg. What is the moment of inertia of this rod for an axis at its center, perpendicular to the rod?
You are a project manager for a manufacturing company. One of the machine parts on the assembly line is a thin, uniform rod that is 60.0 cm long and has mass 0.400 kg. One of your engineers has proposed to reduce the moment of inertia by bending the rod at its center into a V-shape, with a 60.0o angle at its vertex. What would be the moment of inertia of this bent rod about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the V at its vertex?
An airplane propeller is 2.08 m in length (from tip to tip) with mass 117 kg and is rotating at 2400 rpm (rev/min) about an axis through its center. You can model the propeller as a slender rod.
(a) What is its rotational kinetic energy?
(b) Suppose that, due to weight constraints, you had to reduce the propeller's mass to 75.0% of its original mass, but you still needed to keep the same size and kinetic energy. What would its angular speed have to be, in rpm?
A compound disk of outside diameter 140.0 cm is made up of a uniform solid disk of radius 50.0 cm and area density 3.00 g/cm2 surrounded by a concentric ring of inner radius 50.0 cm, outer radius 70.0 cm, and area density 2.00 g/cm2. Find the moment of inertia of this object about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the object and passing through its center.
A wheel is turning about an axis through its center with constant angular acceleration. Starting from rest, at t = 0, the wheel turns through 8.20 revolutions in 12.0 s. At t = 12.0 s the kinetic energy of the wheel is 36.0 J. For an axis through its center, what is the moment of inertia of the wheel?
