Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Relative Velocity
Relative velocity is the velocity of an object as observed from a particular reference frame. In this scenario, the woman’s walking speed is relative to the moving sidewalk, which means her effective speed when walking in the same direction as the sidewalk is the sum of her walking speed and the sidewalk's speed.
Recommended video:
Intro to Relative Motion (Relative Velocity)
Distance and Time Relationship
The relationship between distance, speed, and time is fundamental in physics, expressed by the formula: distance = speed × time. To find the time taken to traverse a distance, one can rearrange this formula to time = distance / speed, which is essential for calculating how long it takes the woman to reach the end of the sidewalk.
Recommended video:
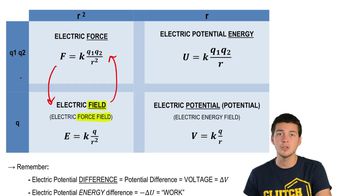
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Constant Speed Motion
Constant speed motion refers to the movement of an object at a fixed speed in a straight line. In this problem, both the moving sidewalk and the woman walking on it are examples of constant speed motion, allowing for straightforward calculations of their combined speeds and the time taken to cover the distance.
Recommended video:
Phase Constant of a Wave Function