Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
RMS Speed
The root mean square (RMS) speed of gas molecules is a measure of the average speed of particles in a gas. It is calculated using the formula v_rms = √(3kT/m), where k is the Boltzmann constant, T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, and m is the mass of a molecule. This concept is crucial for understanding how temperature affects molecular motion.
Recommended video:
Temperature and Kinetic Energy
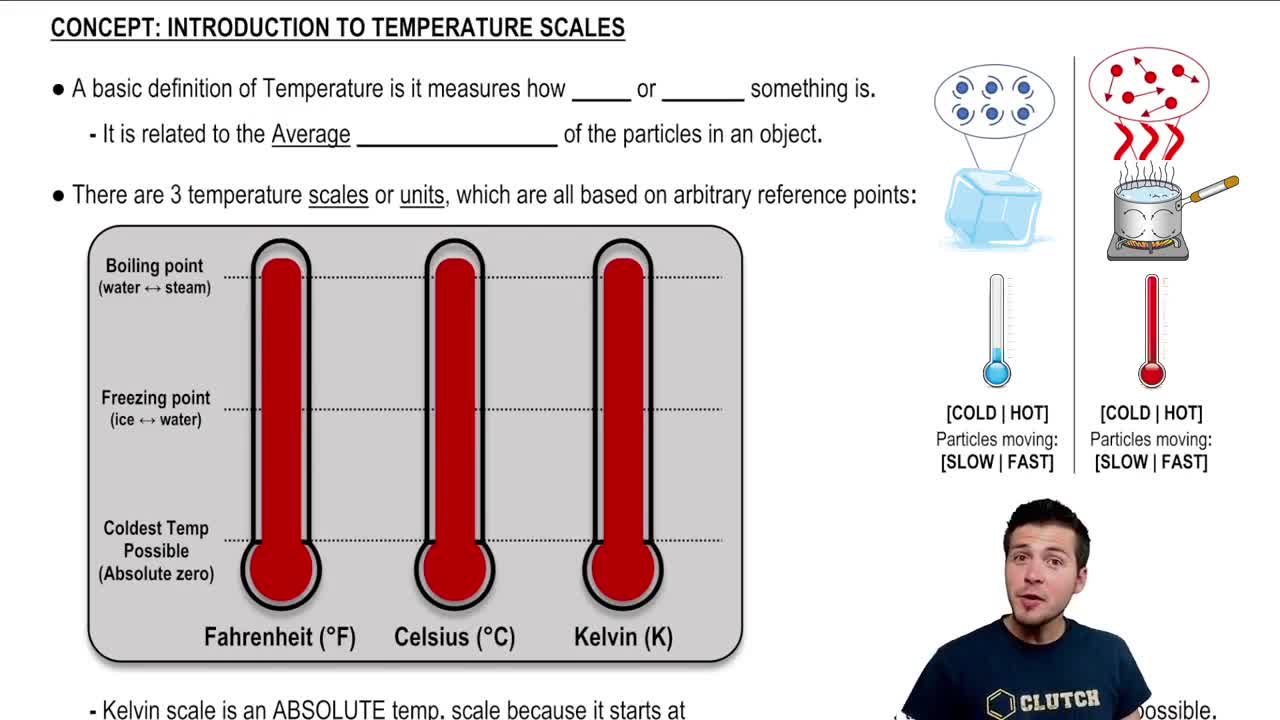
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the molecules also increases, leading to higher speeds. This relationship is fundamental in thermodynamics and helps explain how changes in temperature influence molecular behavior.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
Absolute Temperature Scale
The absolute temperature scale, measured in Kelvin (K), is essential for calculations involving gas laws and molecular speeds. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15. Understanding this scale is necessary for accurately determining the RMS speed when temperatures are given in Celsius.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales