Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. In thermodynamics, it quantifies the amount of energy in a system that is not available to do work. When a system undergoes a change, such as cooling, the entropy can either increase or decrease depending on the direction of heat transfer and the nature of the process.
Recommended video:
Thermodynamic Processes
Thermodynamic processes describe the changes in state variables of a system, such as temperature, pressure, and volume. In this scenario, the cooling of the gas represents a process where heat is removed from the system, affecting its internal energy and entropy. Understanding whether the process is reversible or irreversible is crucial for calculating the entropy change accurately.
Recommended video:
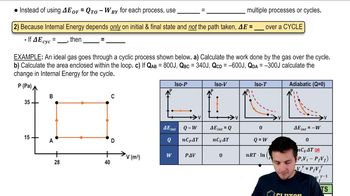
Properties of Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. It implies that natural processes tend to move towards a state of maximum entropy. In this question, the entropy change of both the gas and the universe must be considered, as the cooling process will affect the entropy of the gas while the water bath remains at a constant temperature.
Recommended video:
Thermal Efficiency & The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance