Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Equilibrium in Fluid Mechanics
In fluid mechanics, equilibrium refers to a state where the net forces acting on an object are balanced, resulting in no acceleration. For the piston in the cylinder, this means that the pressure exerted by the gas on one side must equal the pressure exerted by the spring and the atmospheric pressure on the other side when the system is at rest.
Recommended video:
Pressure and Force Relationship
Pressure is defined as force per unit area (P = F/A). In the context of the piston, the pressure in the gas chamber exerts a force on the piston that can be calculated by multiplying the pressure by the cross-sectional area of the piston. Understanding this relationship is crucial for determining the net force acting on the piston when it is displaced.
Recommended video:
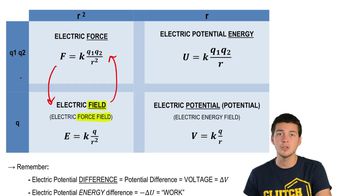
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Ideal Gas Law and Temperature Effects
The Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT) describes the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas. In this scenario, it is important to recognize that the gas remains at a constant temperature, which implies that any changes in pressure due to the movement of the piston will be directly related to changes in volume, affecting the net force on the piston.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance