Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion refers to the increase in volume of a substance as its temperature rises. In the context of thermometers, liquids like ethyl alcohol expand significantly more than the glass of the thermometer itself. This property allows the liquid to rise in the capillary tube, providing a visual indication of temperature changes.
Recommended video:
Capillary Action
Capillary action is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of external forces. In thermometers, this phenomenon allows the alcohol to rise in the narrow capillary tube when heated. The height of the liquid column is directly related to the temperature, as the liquid expands and moves upward.
Recommended video:
Newton's Third Law & Action-Reaction Pairs
Temperature Scale
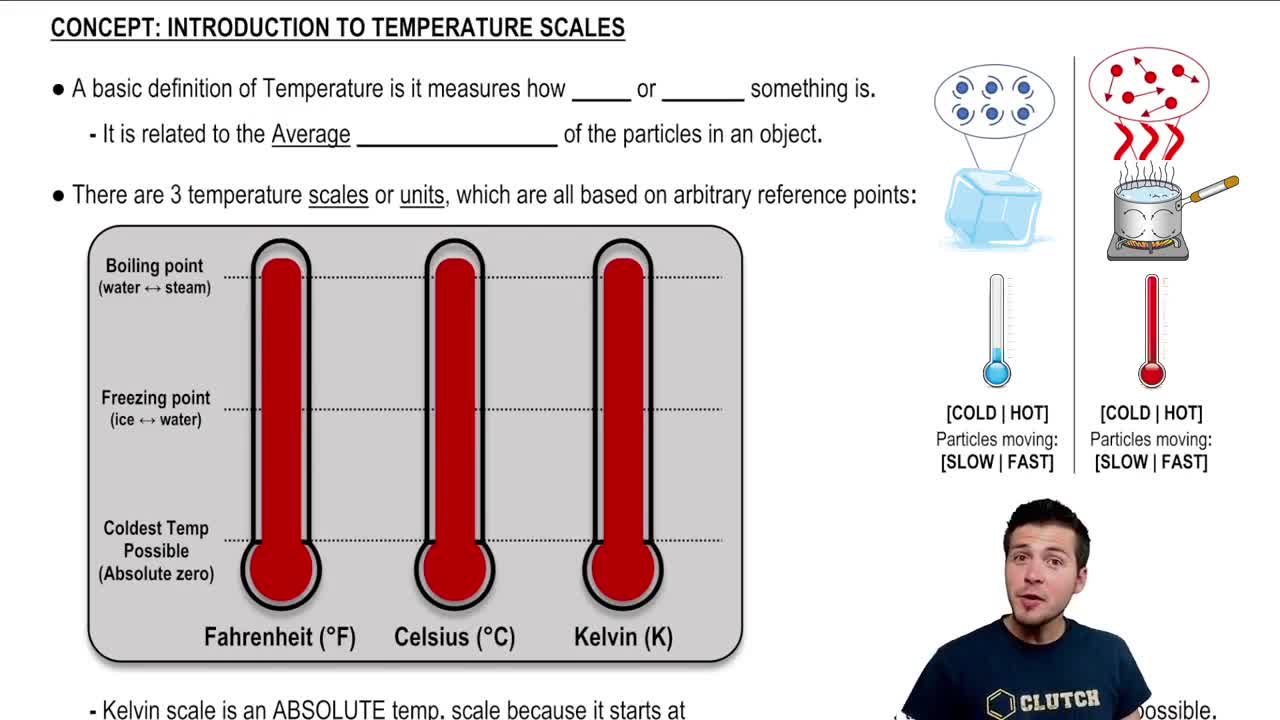
The temperature scale is a system for measuring temperature, commonly using degrees Celsius (°C). In this problem, the relationship between the height of the alcohol column and temperature is linear, allowing for the calculation of temperature based on the change in height. Understanding this relationship is crucial for determining the temperature corresponding to the new height of the alcohol column.
Recommended video:
Introduction To Temperature Scales
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance