Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hooke's Law
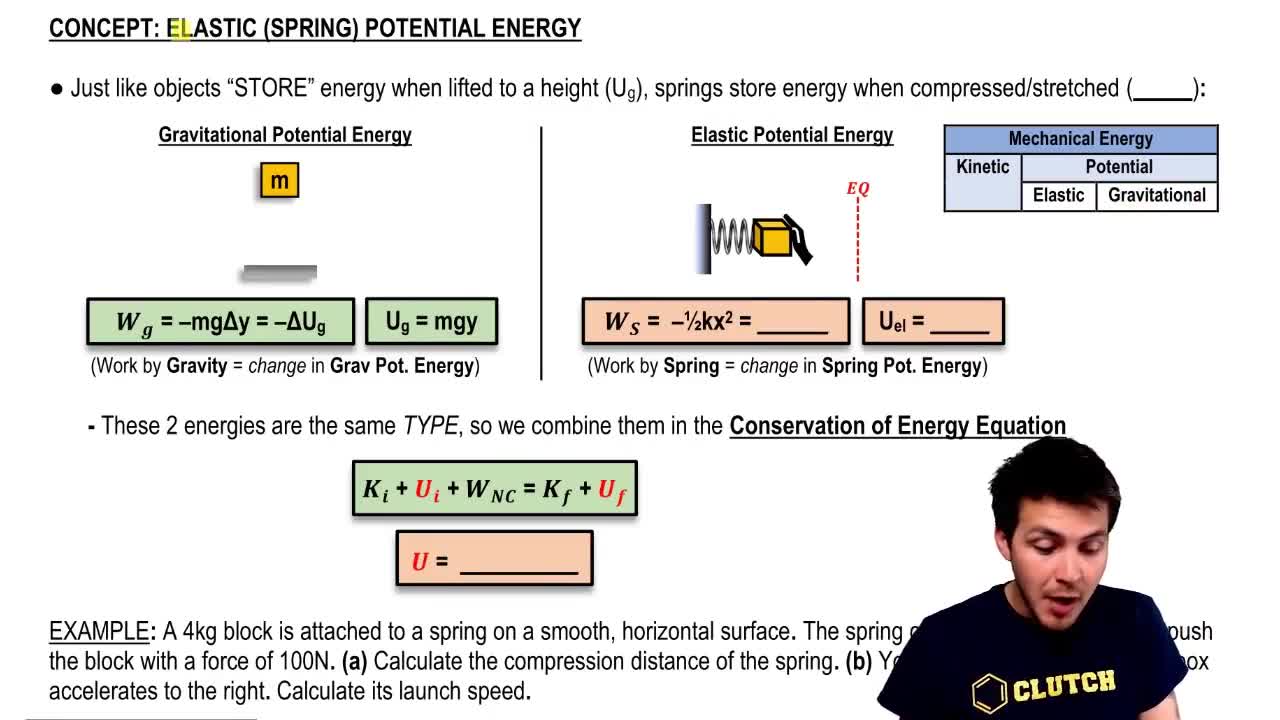
Hooke's Law states that the force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to its displacement from the equilibrium position, expressed as F = -kx, where k is the spring constant. This principle is fundamental in understanding how springs store potential energy when displaced from their rest position.
Recommended video:
Spring Force (Hooke's Law)
Potential Energy in Springs
The potential energy (PE) stored in a spring is given by the formula PE = 1/2 kx², where x is the displacement from the equilibrium position. This energy is maximum when the spring is fully compressed or stretched and decreases as the spring returns to its equilibrium position, converting potential energy into kinetic energy.
Recommended video:
Energy in Horizontal Springs
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy of an object due to its motion, calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 mv², where m is mass and v is velocity. In the context of a mass on a spring, as the mass moves through the equilibrium position, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, reaching maximum kinetic energy when the displacement is zero.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy