Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy (U) is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. It is calculated using the formula U = -G(m1*m2)/r, where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between their centers of mass. This concept is crucial for understanding how mass interacts with gravity and how energy is stored in gravitational fields.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
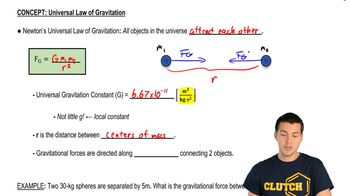
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation states that every point mass attracts every other point mass in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This law provides the foundation for calculating gravitational forces and potential energy in systems involving multiple masses, such as the particle and cylinder in the question.
Recommended video:
Universal Law of Gravitation
Distance in Gravitational Calculations
In gravitational calculations, the distance between the centers of mass of the interacting bodies is critical. For a particle outside a cylinder, the effective distance used in potential energy calculations must account for the geometry of the system. Understanding how to determine this distance, especially when the particle is outside the cylinder, is essential for accurately calculating the gravitational potential energy.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Forces in 2D
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance