Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buoyancy
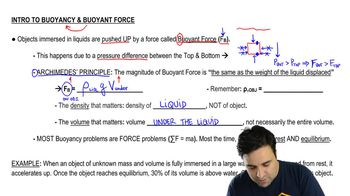
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object submerged in it. This force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object, as described by Archimedes' principle. In this scenario, the cone experiences a buoyant force that balances its weight, determining how much of it is submerged and how much is above the liquid.
Recommended video:
Intro to Buoyancy & Buoyant Force
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is a critical factor in determining whether an object will float or sink in a fluid. The densities of the cone (p₀) and the liquid (pᵦ) influence the buoyant force acting on the cone. If the density of the cone is less than that of the liquid, it will float, and the ratio of the heights will depend on these densities.
Recommended video:
Height Ratio (h/l)
The height ratio (h/l) represents the proportion of the cone's height that is exposed above the liquid compared to its total height. This ratio can be derived from the balance of forces acting on the cone, specifically the relationship between the buoyant force and the weight of the cone. Understanding this ratio is essential for solving the problem and determining how much of the cone is submerged.
Recommended video:
Ratio of energies of cylinder on surface