Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gravitational Potential Energy (Ug)
Gravitational potential energy (Ug) is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. It is calculated using the formula Ug = mgh, where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s²), and h is the height above a reference point. In this context, the height is the distance the water falls, which is 25 m.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
Energy Conservation
The principle of energy conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In the case of the hydroelectric dam, the gravitational potential energy of the falling water is converted into kinetic energy as it falls, and then into mechanical energy as it spins the turbine, ultimately generating electrical energy.
Recommended video:
Conservation Of Mechanical Energy
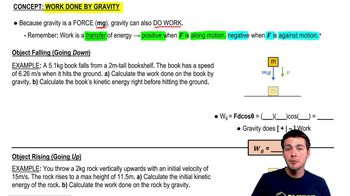
Work Done by Gravity
The work done by gravity on an object is equal to the change in gravitational potential energy as the object moves in the gravitational field. For the falling water, the work done by gravity can be calculated as the product of the weight of the water and the height it falls. This work is what allows the water to do useful work on the turbine, contributing to electricity generation.
Recommended video: