Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Work Done by Gravity
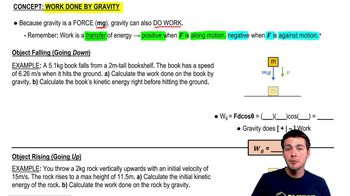
The work done by gravity on an object is calculated using the formula W = mgh, where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the vertical displacement. In this scenario, the vertical height change must be determined from the initial and final positions to find the work done against gravitational force.
Recommended video:
Displacement Vector
Displacement is a vector quantity that represents the change in position of an object. It is defined by the difference between the final and initial position vectors. In this case, the displacement vector can be calculated by subtracting the initial position vector from the final position vector, which helps in determining the vertical component necessary for calculating work done by gravity.
Recommended video:
Displacement vs. Distance
Inclined Plane Dynamics
An inclined plane affects the forces acting on an object, including gravitational force and friction. The angle of the incline influences the component of gravitational force acting parallel and perpendicular to the surface. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for analyzing the work done by gravity as the compressor moves up the incline.
Recommended video: