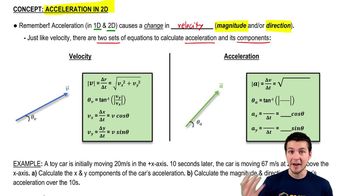
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Angular Velocity
Angular velocity is a measure of how quickly an object rotates around an axis, expressed in radians per second. In this question, the angular velocity ω is given as a function of time, indicating that it changes as time progresses. Understanding how to differentiate this function is crucial for finding the angular acceleration and subsequently the tangential acceleration.
Recommended video:
Intro to Angular Momentum
Tangential Acceleration
Tangential acceleration refers to the rate of change of the linear velocity of a point on a rotating object. It can be calculated using the formula a_t = r * α, where r is the radius and α is the angular acceleration. This concept is essential for determining how quickly a point on the gear is speeding up or slowing down as it rotates.
Recommended video:
Angular Acceleration
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity over time, typically expressed in radians per second squared. It can be derived by differentiating the angular velocity function with respect to time. In this problem, calculating angular acceleration is necessary to find the tangential acceleration of a tooth on the gear at a specific time.
Recommended video:
Conservation of Angular Momentum