Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration directed towards the center of a circular path that an object follows. It is necessary for maintaining circular motion and is calculated using the formula a = v²/r, where v is the tangential velocity and r is the radius of the circular path. In the context of a centrifuge, this acceleration increases with both the speed of rotation and the distance from the axis.
Recommended video:
Intro to Centripetal Forces
Tangential Velocity
Tangential velocity is the linear speed of an object moving along a circular path, measured at any point along the circumference. It can be calculated from the rotational speed (in revolutions per minute) and the radius of the circular path. For a centrifuge, the tangential velocity at the end of a test tube can be derived from the rotation speed and the distance from the axis, which is crucial for determining the centripetal acceleration.
Recommended video:
Calculating Velocity Components
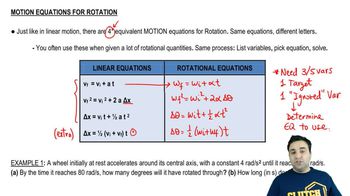
Rotational Motion
Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object that rotates around an axis. In a centrifuge, the test tubes experience rotational motion, which results in forces acting on the contents due to the rapid spinning. Understanding the principles of rotational motion, including angular velocity and the relationship between linear and angular quantities, is essential for calculating the effects of this motion, such as the acceleration experienced by the test tubes.
Recommended video:
Equations of Rotational Motion
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance