9. Work & Energy
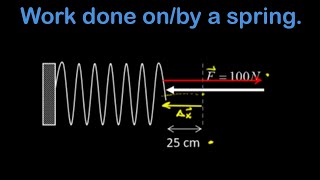
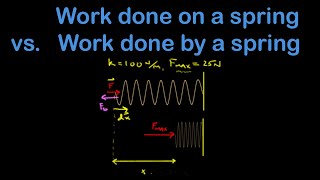
Work By Springs
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceA massless spring with spring constant is suspended from the ceiling. A student carefully hangs a mass from the free end. How long is the spring now?837views
- Multiple ChoiceJustin slides a block of wood across a frictionless tabletop at . It collides with a horizontal spring which compresses as the block comes to rest. What is the spring constant of the spring?885views
- Multiple ChoiceAn ideal spring with original length of and spring constant of is stretched to a length of . How much work must you do on the spring to stretch it an additional ?917views
- Multiple ChoiceA spring-loaded toy gun shoots a metal ball at . How much energy was stored in the spring when it was cocked, and ready to shoot?992views
- Textbook Question
A -kg box moving at m/s on a horizontal, frictionless surface runs into a light spring of force constant N/cm. Use the work–energy theorem to find the maximum compression of the spring.
2647views - Textbook Question
A surgeon is using material from a donated heart to repair a patient's damaged aorta and needs to know the elastic characteristics of this aortal material. Tests performed on a -cm strip of the donated aorta reveal that it stretches cm when a -N pull is exerted on it. If the maximum distance it will be able to stretch when it replaces the aorta in the damaged heart is cm, what is the greatest force it will be able to exert there?
866views - Textbook Question
A surgeon is using material from a donated heart to repair a patient's damaged aorta and needs to know the elastic characteristics of this aortal material. Tests performed on a -cm strip of the donated aorta reveal that it stretches cm when a -N pull is exerted on it. What is the force constant of this strip of aortal material?
1198views - Textbook Question
(II) A spring has k = 65 N/m . Draw a graph like that in Fig. 7–11 and use it to determine the work needed to stretch the spring from x = 3.0cm to x = 7.5cm, where x = 0 refers to the spring’s unstretched length.
816views